Abstract
In the current work, we used molecular approaches to collect and characterise bacteria that produce amylase from soil. Based on clear zones, three species were separated using iodine agar plates. Then, these bacterial isolates were characterised by 16S rRNA gene sequencing. Based on 16S rRNA analysis, the bacterial isolates were identified as Bacillus cerus, Bacillus subtilis, and Bacillus stratosphericus. In addition, numerous growth parameters were tuned to produce the most amylase possible. For both 24 and 48 hours, the isolates' maximum optical density for growth was seen at pH 7.0. Compared to nitrogen and peptone, all three of the bacterial isolates produced the greatest amount of amylase when maltose was utilised as the carbon source. Further investigation is needed to determine which novel isolates in this site have the highest amylase activity. Our findings indicate that this enzyme has a variety of potential industrial applications.
Key Words
Amylase, Optical Density, Enzyme Assay, Bacillus Cerus, Bacillus Subtilis, Bacillus Stratosphericus
Introduction
Enzyme
The majority of chemical reactions required to sustain life are catalysed by enzymes, which are biological macromolecules that resemble proteins with the exception of catalytic RNA molecules (ribozymes). According to Singh et al. (2016), enzymes are vital macromolecules that sustain life since they are incredibly selective and only increase the rate of a given chemical or biological reaction by lowering the activation energy without causing any long-term changes in them (Kumar & Mehta, 2013).Since all of the metabolic processes in a normal cell depend on them to happen at rates high enough for life, they are also referred to as "biocatalysts" (Gurung et al., 2013)
History of Enzyme Discovery
Enzyme use and its history have been widely recognised for several centuries. For example, the enzymes assisted in the preservation of food and drink in ancient Egyptian societies. Enzymes have also been used continuously in the production of cheese from approximately 400 BC. But according to Gurung et al. (2013), Wilhelm Friedrich Kuhne, a German physiologist at Heidelberg University, is credited with coining the term "enzyme" and using it for the first time in 1877. But the enzyme was first isolated and crystallised in 1926 by James B. Summer of Cornell University. It was his goal to win him the 1947 Nobel Prize. In 1972, Worthington Biochemical Corporation was founded.
Structure of an Enzyme
Generally globular in shape, enzymes can be distinguished from fibrous proteins by the stable three-dimensional structure and interaction of certain secondary structural components (Ray 1961). According to Bonham & Strand (1963) their molecular weight ranges from roughly 10,000 to millions. These are heavy-molecule compounds mostly made up of chains of amino acids joined by peptide bonds (Berg & Prockop (1973).Because of their catalytic activity, all proteins are not enzymes, but all enzymes are proteins. The active enzyme site, which makes up only 10–20% of the overall enzyme size, is the region of the tertiary enzyme structure that is responsible for catalytic activity. The active site is often a hydrophilic hole or cavity that holds the enzymatic response and is made up of several side chains of amino acids that link the substrate.
Figure 1
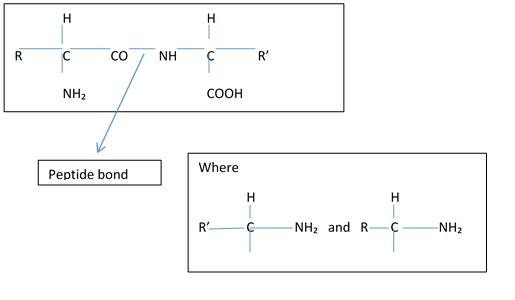
Sometimes the enzyme also needs a non-protein component to carry out the reaction—a co-enzyme, in the case of an organic vitamin-based molecule, or a co-factor, in the case of a metallic ion. In this case, the non-protein component could be referred to as a prosthetic group, the protein portion as an apoenzyme, and the total enzyme as a holoenzyme (Vigneshwaran et al., 2010)
Figure 2
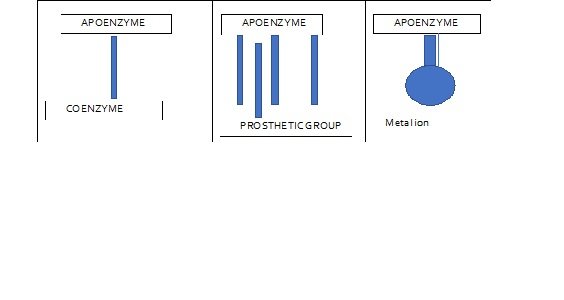
The roles of the enzymes are very diverse. All of the vital chemical changes required for life are caused by these enormous biological molecules (Gurung et al., 2013) For example, these enzymatic catalysts mediate the process of continual physical and chemical change that is known as metabolism, which is the culmination of all the biochemical events that occur within each cell of a living creature ((Berg & Prockop (1973). It is estimated that about 4,000 biological reactions are catalysed by enzymes. Enzymes play a very selective catalytic role, which dramatically accelerates the rate and specificity of metabolic reactions.
Enzymes aid in a variety of processes, including as waste disposal, DNA synthesis, building new tissue and repairing damaged tissue, digestion, and reproduction (Gurung et al., 2013; Worthington Biochemical Corporation, 1972).
The roles of the enzymes are very diverse. All of the vital chemical changes required for life are caused by these enormous biological molecules (Gurung et al., 2013) For example, these enzymatic catalysts mediate the process of continual physical and chemical change that is known as metabolism, which is the culmination of all the biochemical events that occur within each cell of a living creature ((Berg & Prockop (1973). It is estimated that about 4,000 biological reactions are catalysed by enzymes. Enzymes play a very selective catalytic role, which dramatically accelerates the rate and specificity of metabolic reactions.
Enzymes aid in a variety of processes, including as waste disposal, DNA synthesis, building new tissue and repairing damaged tissue, digestion, and reproduction (Gurung et al., 2013; Worthington Biochemical Corporation, 1972).
Classification of Enzymes
there was no appropriate database, there was a great deal of misunderstanding over the names of the enzymes before the enzyme nomenclature committee was formed. The nomenclature of enzymes used to be troublesome as well; in order to make sense of them, trivial names were given to them. Occasionally, distinct groups of biochemists might give the same enzyme various names; unique enzymes have also been given the same names. It was necessary to create a method to precisely name and categorise enzymes in order to address this confusion. [The Enzyme Function Classification and Evolution]
Enzyme nomenclature guidelines have been created by the International Union of Biochemistry (I.U.B.) with the aim of representing both the substrate and the type of reaction catalysed (Miller, 1972).
According to the enzyme commission, the enzymes are classified into 6 different classes.
Table 1
|
Enzyme commission number |
Enzyme class |
Type of Reaction |
Example |
|
E.C .1 |
Oxidoreductases |
Oxidation / reduction |
Alcohol
dehydrogenases |
|
E.C . 2 |
Transferases |
Group /atom transfer |
Aminotransferases
|
|
E.C. 3 |
Hydrolases |
Hydrolysis |
Amylases |
|
E.C. 4 |
Lyases |
Group removal |
Pectate
lyases |
|
E.C. 5 |
Isomerases |
Isomerization |
Mutases |
|
E.C. 6 |
Ligases |
Joining of molecules connected to the
pyrophosphate bond rupture. |
DNA ligases
|
Many important enzymes, including cellulases, amylases, proteases, and xylanases, are today useful to the industrial sectors for a variety of commercial purposes. According to Singh et al. (2015), ?-amylase stands out among the extremely adaptable enzymes for commercial uses because of the abundance of starch available on Earth. It can be used for a variety of purposes, including the synthesis of glucose and corn syrups, biofuel, and the pharmaceutically significant cyclodextrin (Sundarram & Murthy, 2014; Tiwari et al., 2015)
Microbial Amylase
It is now widely acknowledged that microorganisms are a rich source of practical enzymes. The study of amylases with microbial origins has been a focus of both scientific and industrial research. Microorganisms might vary in their amylase production from genus to even within the same species. Furthermore, the origin of the microbe affects amylase synthesis as well; strains isolated from starchy environments produce larger levels of the enzyme. Modern genetic engineering methods have made it possible to improve microbial strains for optimal enzyme output (Gopinath et al., 2017). Remarkably, the first commercially manufactured enzyme of a microbial source was an amylase of fungal origin in 1894 and it is used for therapeutic purposes to cure digestive disorder (Singh et al., 2016)
Many living things, including humans, plants, and microbes like bacteria, fungus, and yeast, produce the amylases that break down starch. The genus Bacillus contains the majority of the microorganisms used in industrial applications, including bacteria (Oluwadamilare
et al., 2019). Due to their diverse nature and exceptional environmental adaptability, Bacillus species exhibit considerable versatility. Their metabolic makeup and the output of enzymes are influenced by a variety of factors (Bozic et al., 2011). It is ubiquitous in nature, dependent on the right nutrients for growth, and produces the greatest amount of alpha amylase (Kalyani and Rajesh, 2018; Karnwal, et al., 2011).
Large-scale industrial synthesis of extracellular enzymes for a variety of applications is facilitated by the use of Bacillus subtilis, B. stearothermophilus, B. amyloliquefaciens, and B. licheniformis (Singh et al., 2015).
Use of Microbial Amylase in Industries
One of the most important enzymes in modern biotechnology is amylase, which is used in many biotechnological processes such as the production of paper, textiles, detergents, food, pharmaceutical, and starch degradation. With over 25% of all enzyme sales, they are among the most significant category of industrial enzymes. The range of applications for amylase has grown to include scientific, medicinal, and analytical chemistry, among many other fields (Madika et al. 2017; Fang et al., 2019).
Amylases can be obtained from multiple sources such as animals, plants and microorganisms. Microbial amylases are able to meet industrial standards due to their minimal budget requirements when produced in big quantities (Vidya et al.,, 2023) has been the method used to obtain all industrial enzymes to date, from cultivated bacteria or fungi. Table 1.2 lists the various industrial industries' usage for amylase (Cloete et al., 2019)
Table 2
|
Domain |
Uses |
|
Food
and brewing Industry |
Starch liquefaction in order to
produce fructose and glucose syrups.control of suspensions' and solutions'
viscosity. Starch is gelatinized to improve thickness or viscosity.Starch is
saccharified to produce glucose and maltose syrups.In order to keep bread
from hardening during baking, moderate starch polymer hydrolysis is used to
reduce staling. |
|
Biofuel
production |
Saccharification and starch
liquefaction to create the fermentable sugars needed to make ethanol. |
|
Pharmaceutical
industry |
Used
in digestive tonics. |
|
Detergent
Industry |
Difficult stains are removed by
breaking down starchy food remnants. |
|
Textile
industry |
De-sizing is the process of
eliminating starch from the cloth, which is needed to make the warp thread
stronger during weaving. |
|
Paper
industry |
Reducing the viscosity of the starch
allows for effective and sufficient treatment of the paper coating, improving
the stiffness and strength of the paper. |
Role of Microotganisms in Producing Useful Enzymes
It has now been established that microorganisms are a valuable source of enzymes. Scientific and industrial sectors have focused mostly on amylases originating from microorganisms. Microorganisms vary in the amount of amylase they produce, even within the same species. Additionally, the synthesis of amylase varies based on the origin of the microbe; strains isolated from starchy environments produce larger levels of the enzyme. It is now possible to improve microbial strains for optimum enzyme yield thanks to sophisticated genetic engineering techniques (Gopinath et al., 2017).
Pathania, et al.(2016) amylase production, it is essential to optimise various growth conditions like temperature, pH, and energy sources.In order to determine the ideal production settings and learn more about the unique strain of amylase that produces high levels of activity and production, numerous investigations on the production of amylase from microbial sources have been carried out.
Pokhrel et al. (2013) investigated the amylolytic activity of four bacterial isolates from sewage. One strain produced the largest clear zone of hydrolysis out of all of these isolates. The strain was used for further research when it was identified as Bacillus sp. The 48-hour incubation period resulted in high enzyme synthesis. At pH 7 and 35ºC, the best enzymatic activity was observed.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain isolated from garden soil was investigated by Raju and Divakar (2013), who also assessed the organism's capacity to hydrolyze starch. The effects of a number of production parameters, including substrate and inoculum concentration, temperature, pH, organic and inorganic source, and carbon sources, were assessed. The highest enzyme production was seen under submerged fermentation conditions when maltose (180±2.6 U/ml) was used as the carbon source, ammonium sulphate (61±3.0 U/ml) as an inorganic nitrogen source, and yeast extract (120±3.6 U/ml) as a nitrogen source.
Rani et al., (2025) additionally, there was a high synthesis of enzymes at pH 7 (226±4.1 U/ml) and temperature 40ºC (120±1.9 U/ml). After 48 hours, the effect of varying incubation times revealed the maximum enzyme activity (162.01±0.56 U/ml), and the optimal concentration level for optimum enzyme synthesis was found to be 5% inoculum concentration, which produced activity of 132±2.00 U/ml.
Seven bacterial species were isolated from soil and tested for amylase production on starch agar medium in a different investigation carried out by Alariya et al. (2013). Only "4" of the isolates turned out to be amylase positive. The strains were identified as Escheritia coli, Bacillus subtilis, Pseudomonas florescens, and Serratia marscens based on their distinguishing characteristics. It was discovered that 35–40ºC was the ideal temperature for production. Maximum growth was noted at 1% dextrose concentration, but it increased with increasing substrate concentration. After 48 hours of incubation and 1 ml of inoculum for optimal growth, it was discovered that pH 7 was the ideal value for enzyme activity.
On a starch agar plate, Singh et al. (2015) screened the soil for microorganisms that produced amylase. They gathered sixty soil samples in all from various sites. 17 pure isolates were amylase positive out of 60 samples. Further analysis was done on the isolates exhibiting the highest levels of amylase activity. We investigated the enzyme's production at several pH and temperature ranges. The genus Bacillus is home to all 17 of the isolates that have been found. At 40 degrees Celsius, the starch hydrolysis zone reached its maximum, and below 35 degrees Celsius, it decreased. At pH 7 and 8, amylase production peaked, and at pH 9 and 10, it started to decline.
Prameela et al. (2016) made an effort to separate amylolytic bacteria from soil in a different investigation. To obtain pure bacterial isolates, they serially diluted the soil sample and then subcultured them on nutrient agar medium for additional research. The isolates exhibiting the biggest zones of clearance were further characterised based on the results of the starch hydrolysis test. Following the performance of biochemical tests, the isolates showed positive results for the Methyl Red, Starch Hydrolysis, Citrate, and Voges Proskauer assays. The isolate was linked to the genus Bacillus, according to the data. Several factors, including pH and carbon sources, that control the growth of isolates were optimized. For 24 hours, the isolate showed its highest activity at pH 7 and 37ºC.
When pomegranate peel powder was used as the carbon source instead of the original carbon sources, the study found that the largest amount of ?-amylase production was produced.
Thus, by modifying the physical parameters in light of earlier research, we have attempted to isolate amylase-producing bacteria while maintaining the previously mentioned optimised parameters and achieving maximum yield.
Materials and Methods
Sample Collection
A sample of the soil was taken in multiple locations throughout Peshawar. The texture, moisture content, and pH of the collected soil samples were analysed. In order to obtain soil samples, the top layer of soil was scraped, and then samples were taken at a depth of around 10 cm. It was kept with the proper tags attached in pre-sterilized plastic bags. The samples were further processed at the IBS, SUIT laboratory.
Preparation and Analysis of Sample
Nine millilitres of sterile distilled water were aseptically filled with one gramme of each sample, which was then serially diluted. Next, bacteria were transferred to nutritional agar media using the spread plate technique, and they were incubated for 24 hours at 37 °C. Further sub-culturing was done on the plates displaying separate colonies of bacteria (Pokhrel et al., 2013).
Starch Hydrolysis Test-Based Screening and Selection of Potent Amylase Producing Bacteria
Bacterial colonies were randomly streaked on freshly produced starch agar plates using a sterile wire loop to screen for amylolytic strains. The plates were then incubated for a full day at 37ºC. To identify amylolytic strains, staining was done using Gram's iodine solution. The colonies' surrounding zone of hydrolysis directed the presence of amylase producers. According to Alariya et al. (2013), isolates with the biggest zone of hydrolysis were chosen for additional study.
Organism Preservation
After being grown in nutrient broth media for a 24h, the purified organisms will be stored in 50% glycerol stock in eppendorf tubes at a temperature of -20 C to ensure their preservation.
Preparation and Analysis of Sample
Each sample weighed one gramme, which was aseptically added to nine millilitres of sterile distilled water and then serially diluted. Following the transfer of bacteria to nutritional agar medium using the spread plate technique, the bacteria were incubated at 37°C for 24 hours. The plates with discrete bacterial colonies underwent additional subculturing (Pokhrel et al., 2013).
Screening and Selection of Potent Amylase Producing Bacteria Using Starch Hydrolysis Test
Bacterial colonies were randomly streaked on freshly produced starch agar plates using a sterile wire loop to screen for amylolytic strains. The plates were then incubated for a full day at 37ºC. To identify amylolytic strains, staining was done using Gram's iodine solution. The colonies' surrounding zone of hydrolysis directed the presence of amylase producers (Alariya et al. 2013; Pathania et al., 2016; Pathania et al., 2017)) isolates with the biggest zone of hydrolysis were chosen for additional study.
Molecular Identification of Bacterial Isolates
The identity of the positive bacterial isolates was verified by molecular identification using 16S rRNA. Macrogen Korea Sequencing Company received a pure culture of positive bacterial isolates for the purpose of extracting DNA and sequencing the 16s rRNA gene. 16s rRNA sequencing was conducted using Universal Primers (27F: AGAGTTTGATCTGGCTCAG) and 1492R: GGTTACCTTGTTACG ACTT. After amplification, the 16S rRNA PCR product was trimmed and sequenced. Using a BLAST search and the maximum aligned 16s rRNA sequences found in the NCBI GenBank, the unknown creature was found. To comprehend the evolutionary relationship, a phylogenetic tree was constructed using MEGA 6.0 software (Xie et al., 2014; Tamura et al., 2007; Hasan et al., 2017)
Production of Enzymes under Optimized Conditions
The fermentation medium was optimised to produce the most cellulase possible. The impact of diverse elements on the generation of cellulase was ascertained through the measurement of enzyme activity at varying pH values (5?9) and temperature ranges (35?50?). The impact of different carbon sources, including the concentration of fructose, lactose, and maltose, was investigated in the production medium. The effects of several nitrogen sources, such as peptone, meat extracts, and yeast extract, on the synthesis of enzymes and the development of bacterial isolates were investigated (Pathak et al., 2014; Pathak et al., 2015)
Results
Molecular Identification of Cellulolytic Bacteria
Molecular identification was used to obtain additional confirmation. For 16S rRNA gene sequencing, a pure culture of chosen isolates was shipped to Macrogen Korea [18]. Sequencing was done using universal primers (Table S7). Sequencing was done on the amplified 16S rRNA PCR product. By employing 16S rRNA sequencing for molecular identification, the isolates that were chosen were identified as B. cerus, B. subtilis, and B. stratosphericus. The best sequence alignment results were reported, and all three of the bacterial sequences were found in NCBI GenBank. To comprehend evolutionary relationships, a phylogenetic tree was built using MEGA 6.0 (Figs. 3–5).
Effect of Carbon Source on Enzyme Production
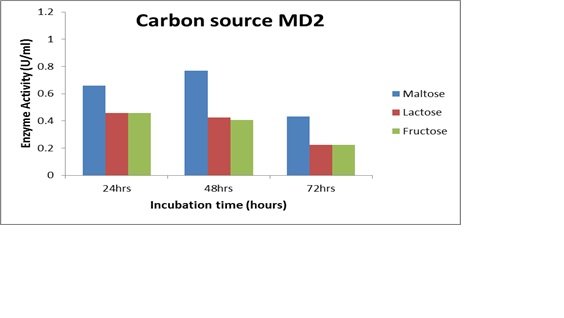
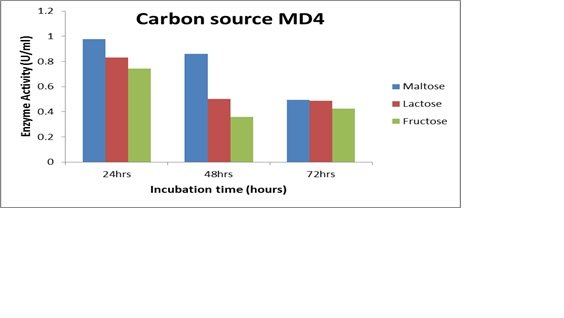
Different carbon sources (lactose, lactose, and fructose) were added to the amylolytic bacteria at 1% concentration and for varying lengths of time (24–72 hours). Photo spectrometer was used to get the results. When maltose was used as a carbon source for 48 hours, maltose was the most effective carbon source for the bacterial strain MB7, to produce the amylase enzyme (Fig. 9A). MD2 demonstrated 24-hour maximum enzyme synthesis when maltose was used as the carbon source (Fig. 9B). For MD4 for a 24-hour period, the highest enzyme activity was produced (Fig. 9C).
Effect of Nitrogen Sources on Enzyme Production
Nitrogen is crucial for the development of enzymes and the proliferation of microorganisms. At 1% concentrations, three distinct nitrogen sources—meat extract, yeast extract, and peptone—were employed. When meat extract was used as a nitrogen source at 48-hour intervals, the bacterial strain MB7 demonstrated optimal enzyme synthesis and peak optical density (Fig. 10A). Using peptone as a nitrogen supply, MD2 recorded the maximum amylase production for 72 hours and the peak optical density for 48 hours (Fig. 10B). When meat extract was used as a nitrogen source for 72 hours, the MD4 bacterial strain likewise showed maximum enzyme activity (Fig. 10C).
Impact of Incubation Time and Temperature on Enzyme Production
For 48 hours at 40°C, MD4 displayed its maximal optical density activity and synthesis of amylase. (Figure 7C). For 72 hours, MB7's maximum cellulose activity was measured at 40°C. At 600 nm, the maximum optical density and maximum MD2 activity were recorded over a 48-hour period at 40? and 400?, respectively (Figs. 7A and 7C).
Mpact of Ph on Enzyme Production
The growing medium pH was one of the most important physical parameters that influenced enzyme secretion. A fermentation was carried out in a shaking incubator for 72 hours in order to determine the optimal pH range for enzyme production. For MD4, the most optimal amylase production was observed at pH 7 for 24 hours, and the perfect growth density was obtained at a peak at pH for 48 hours (Fig. 8C). The maximum amylase production and optical growth density of MB7 at pH 7 over a 48-hour period are displayed in Figure 7A. Over the course of 24 hours, the maximum optical growth density and peak enzyme production for MD2 were seen at pH 5 (Fig. 7B).
Discussion
There is a lot of biological waste in the natural world that microorganisms can use to survive and eventually transform waste materials into less hazardous or valuable goods. Bacteria that produce amylase were isolated from their native habitat for the current investigation. Three bacterial isolates with the ability to manufacture the amylase enzyme, which converts starch to reducing sugar, were obtained from the natural environment for this investigation. Afterwards, 16S rRNA gene sequencing was used to validate the identities of these isolates as B. cerus, B. subtilis, and B. stratosphericus.
The ability of amylase-producing bacterial isolates to form a distinct zone on an iodine agar plate, signifying their capacity to break down starch, allowed for their identification. Several growth factors, including pH, temperature, incubation time, substrate concentration, and carbon sources, were optimised in order to maximise amylase output.
One of the primary sources of nutrients and energy for microorganism growth is the soil. In soil, B. cerus and B. subtilis are the most prevalent organisms. Studies have shown that temperature has a significant impact on microbial growth and, eventually, the generation of extracellular enzymes. Keeping this in mind, the chosen strains were given various circumstances depending on variations in temperature range. At 40°C and 1% starch content, a notable rise in the amount of enzyme synthesis was seen. The pH of each of the three isolates was assessed because prior research has shown that pH affects enzyme synthesis in addition to carbon and temperature. It's interesting to note that all of the isolates that were chosen showed their greatest activity at pH 7 (8C). The results obtained thus far for several Bacillus strains are consistent with those of previous studies.
Different sources of carbon are preferred by different bacteria for growth. In the present work, MD4 was found to exhibit maximum growth and enzyme activity when maltose was used as a carbon source for a full day. Furthermore, when meat extract was used as a nitrogen source for 48 hours of incubation, MB7 exhibited peak activity. Three distinct amylolytic bacteria (Bacillus cereus, Bacillus subtilis, and Bacillus stratosphericus) were identified from sawdust in the Peshawar region in this study, which is the only one of its kind. In order to maximise the synthesis of enzymes, many growth factors (temperature, pH, incubation time, nitrogen, and carbon sources) were optimised in the laboratory.
Figure 3
Bacillus Cerus phylogenetic study using maximum likelihood approach
Figure 4
Bacillus Subtilis phylogenetic study using maximum likelihood approach
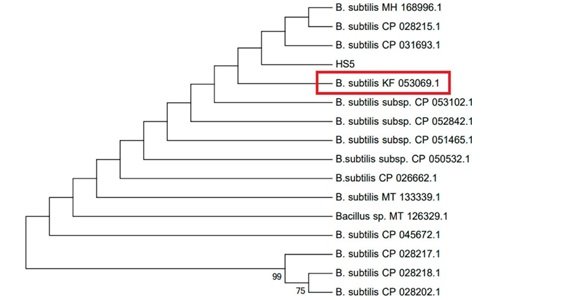
Figure 5

Figure 6

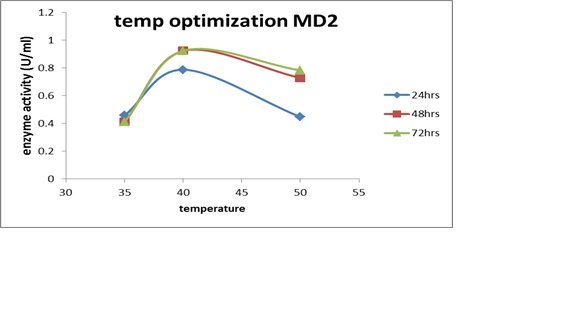
Figure 7
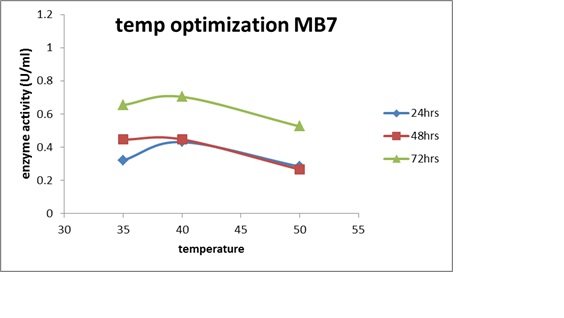
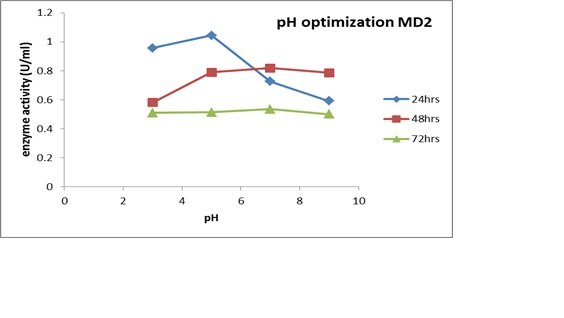
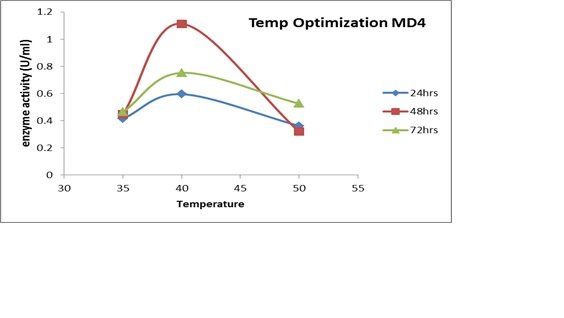
Figure 8
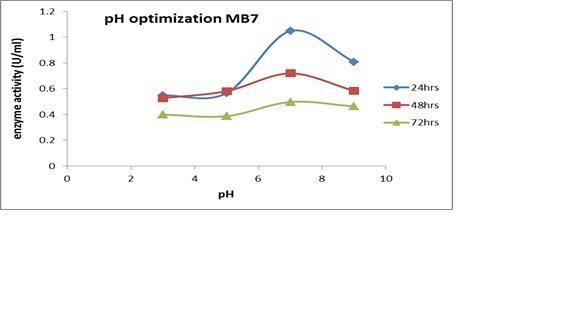
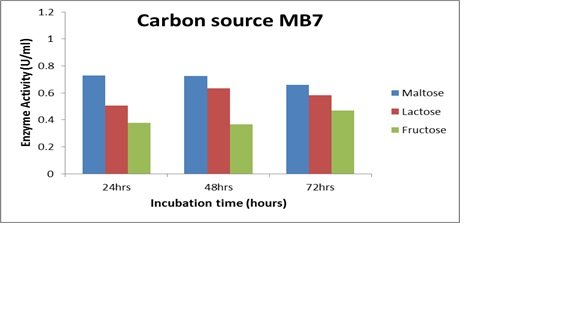
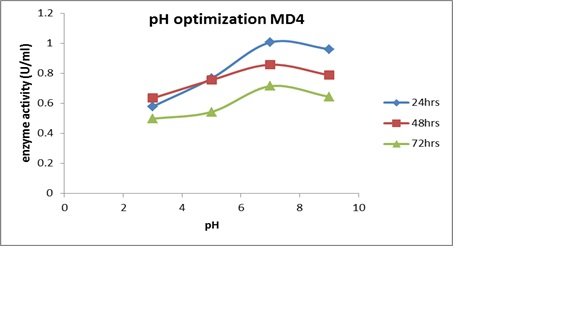
Figure 9
Effects of Carbon source and duration of incubation on enzyme activity and time for MB7, MB2, and MD4 (A, B, and C).
References
- Alariya, S. S., S. Sethi, S. Gupta & Lal, G. (2013). Amylase activity of a starch degrading bacteria isolated from soil. Arch Appl Sci Res., 5(1): 15-24.
- Berg, R. A., & Prockop, D. J. (1973). Purification of carbon-14-labeled protocollagen and its hydroxylation by prolyl-hydroxylase. Biochemistry, 12(18), 3395-3401.
- Bonham, R. A., & Strand, T. G. (1963). Analytical expressions for potentials of neutral Thomas—Fermi—Dirac atoms and for the corresponding atomic scattering factors for X rays and electrons. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 39(9), 2200- 2204.
- Bozic, N., J. Ruiz, J. L. Santin &Z. Vujcic. (2011). Optimization of the growth and α-amylase production of Bacillus subtilis IP 5832 in shake flask and laboratory fermenter batch cultures. J.Serb.Chem.Soc., 76 (7): 965–972.
- Cloete, W. J., Hayward, S., Swart, P., & Klumperman, B. (2019). Degradation of proteins and starch by combined immobilization of protease, α-amylase and β-galactosidase on a single electrospun nanofibrous membrane. Molecules, 24(3), 508.
- De- Souza, P. M. & Oliveira Magalhaes. (2010). Application of microbial α-amylase in industry - A review. Braz J Microbiol., 41: 850-861.
- Fang, W., Xue, S., Deng, P., Zhang, X., Wang, X., Xiao, Y., & Fang, Z. (2019). AmyZ1: a novel α-amylase from marine bacterium Pontibacillus sp. ZY with high activity toward raw starches. Biotechnology for biofuels, 12, 1-15.
- Gopinath, S. C., P. Anbu, M. Arshad, T. Lakshmipriya, C. H. Voon, U. Hashim & Chinni, S. V. (2017). Biotechnological processes in microbial amylase production. BioMed Res Int, 1-9.
- Hasan, M. M., L. W. Marzan, A. Hosna, A. Hakim & Azad, A. K. (2017). Optimization of some fermentation conditions for the production of extracellular amylases by using Chryseobacterium and Bacillus isolates from organic kitchen wastes. J Genet Eng Biotechnol., 15(1), 59-68.
- Kalsoom, M., Rehman, F. U., Shafique, T. A. L. H. A., Junaid, S. A. N. W. A. L., Khalid, N., Adnan, M., & Ali, H. (2020). Biological importance of microbes in agriculture, food and pharmaceutical industry: A review. Innovare Journal of Life Sciences, 8(6), 1-4.
- Kalyani, G., & Rajesh. E. (2018). Production and purification of amylase from Bacillus subtilis isolated from soil. Int J E., 8(3), 246-254.
- Karnwal, A. (2011). Screening and optimization of extracellular amylase production from plant growth promoting Rhizobacteria. Ann.Food.Sci.Techno, 12(2), 135-141.
- Kumar, R., & Mehta, A. (2013). Isolation, optimization and characterization of α- amylase from Bacillus alcalophilus. Int J Sci Res., 2(7), 171-174.
- Madika, A., Ameh, J. B., & Machido, D. A. (2017). Isolation and screening of Bacillus subtilis from soil for amylase production. UMYU Journal of Microbiology Research (UJMR), 2(2), 82-86.
- Miller, E. J. (1972). Structural studies on cartilage collagen employing limited cleavage and solubilization with pepsin. Biochemistry, 11(26), 4903-4909.
- Oluwadamilare, L. A., Dzorbenya, A. G., & Adekunle, F. (2019). A review of literature on isolation of bacteria α-amylase. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol, 6(1), 1333-1342.
- Pathak, S., & Narula, N. (2013). Optimization of pH for the production of amylase by soil mycotic flora of Jabalpur region. Res Rev J Microbiol Biotechnol., 2(1), 17-22.
- Pathak, S. S., S. Kumar, R. C. Rajak, & Sandhu, S. S. (2014). Study of effect of temperature on amylase production by soil mycotic flora of Jabalpur region. World J Pharm Pharm Sci., 3(9), 1448-1458.
- Pathania, S. H. R. U. T. I., Sharma, N., & Handa, S. H. W. E. T. A. (2017). Optimization of culture conditions for production of amylase by Bacillus amyloliquifaciens SH8 using response surface methodology. In Proc Indian Natl Sci Acad 83, 203-210.
- Pokhrel, B., P. Wanjare, S. Singh, B. Purushotham & Kumara, S. (2013). Isolation, screening and characterization of promising α-amylase producing bacteria from sewage enriched soil. Int J Adv Biotechnol Res., 4(2), 286-290.
- Prameela, G., K. P. Dharshini, M. Chidanandappa & Kamala, K. (2016). Isolation and characterization of amylase producing bacteria from orange and pomegranate peel. Indo Am.J.Pharm.Res., 6(11), 7111-7118.
- Raju, E. V. N., & Divakar, G. (2013). Production of amylase by using Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Isolated from Garden Soil. Int.J.Adv.Pharm.Bio.Chem. 2(1), 50-56.
- Rani, K., Rana, R., & Datt, S. (2015). Review on characteristics and application of amylases. Inter. J. Microbiol. Bioinfor, 5(1), 1-5.
- Ray Jr, W. J., & Koshland Jr, D. E. (1961). A method for characterizing the type and numbers of groups involved in enzyme action. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 236(7), 1973-1979.
- Robinson, P. K. (2015). Enzymes: principles and biotechnological applications. Essays in biochemistry, 59, 1.
- Singh, R., A. Mittal, M. Kumar., & Mehta, P. (2016). Amylases: A note on current applications. Int.Res.J.Biological.Sci, 5(11), 27-32.
- Singh, V., R. Sharma., & Sharma, P. (2015). Isolation, screening and optimization of amylase producing Bacillus sp. from soil. A.P.J.H.S., 2(3), 94-103.
- Sundarram, A., & Murthy, T. P. K. (2014). α- amylase production and applications: a review. Journal of Applied & Environmental Microbiology, 2(4), 166- 175.
- Tamura, K., J. Dudley, M. Nei & Kumar, S. (2007). MEGA4: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol., 24(8), 1596- 1599.
- Tiwari, S. P., Srivastava, R., Singh, C. S., Shukla, K., Singh, R. K., Singh, P., & Sharma, R. (2015). Amylases: an overview with special reference to alpha amylase. J Global Biosci, 4(1), 1886-1901.
- Vidya, J., RekhaMol, K. R., Vaz, R. G., Madhu, A. G., Mathew, G. M., Binod, P., & Sindhu, R. (2023). Industrial Amylase Production Using Agri-Food Wastes. In Microbial Bioprocessing of Agri-food Wastes (49- 81). CRC Press.
- igneshwaran, C., Shanmugam, S., & Kumar, T. S. (2010). Screening and characterization of keratinase from Bacillus licheniformis isolated from Namakkal poultry farm. Researcher, 2(4), 89-96.
- Xie, F., S. Quan, D. Liu, H. Ma, F. Li, F. Zhou & Chen, C. (2014). Purification and characterization of a novel α-amylase from a newly isolated Bacillus methylotrophicus strain P11-2. Process Biochem, 49(1), 47-53.
Cite this article
-
APA : Ikram, H., Umer, A., & Kashif, M. (2023). Molecular Characterization and Evaluation of Amylase Producing Bacteria from Soil. Global Immunological & Infectious Diseases Review, VIII(I), 12-27. https://doi.org/10.31703/giidr.2023(VIII-I).03
-
CHICAGO : Ikram, Hira, Aiman Umer, and Muhammad Kashif. 2023. "Molecular Characterization and Evaluation of Amylase Producing Bacteria from Soil." Global Immunological & Infectious Diseases Review, VIII (I): 12-27 doi: 10.31703/giidr.2023(VIII-I).03
-
HARVARD : IKRAM, H., UMER, A. & KASHIF, M. 2023. Molecular Characterization and Evaluation of Amylase Producing Bacteria from Soil. Global Immunological & Infectious Diseases Review, VIII, 12-27.
-
MHRA : Ikram, Hira, Aiman Umer, and Muhammad Kashif. 2023. "Molecular Characterization and Evaluation of Amylase Producing Bacteria from Soil." Global Immunological & Infectious Diseases Review, VIII: 12-27
-
MLA : Ikram, Hira, Aiman Umer, and Muhammad Kashif. "Molecular Characterization and Evaluation of Amylase Producing Bacteria from Soil." Global Immunological & Infectious Diseases Review, VIII.I (2023): 12-27 Print.
-
OXFORD : Ikram, Hira, Umer, Aiman, and Kashif, Muhammad (2023), "Molecular Characterization and Evaluation of Amylase Producing Bacteria from Soil", Global Immunological & Infectious Diseases Review, VIII (I), 12-27
-
TURABIAN : Ikram, Hira, Aiman Umer, and Muhammad Kashif. "Molecular Characterization and Evaluation of Amylase Producing Bacteria from Soil." Global Immunological & Infectious Diseases Review VIII, no. I (2023): 12-27. https://doi.org/10.31703/giidr.2023(VIII-I).03
