Abstract
Diabetes mellitus is one of the most frequently encountered diseases in human history, and it is triggered mostly by two factors: one is genetic and the other environmental. According to the World Health Organization, one in every four individuals is diabetic or pre-diabetic, which is a frightening statistic. During the Coronavirus pandemic, there is also a significant setback in the management of diabetes due to lockdown, many diabetes patients suffered greatly, and unfortunately, a large number of elderly diabetics kicked the bucket after contracting SARSCoV-2 last year as their already compromised immune system couldn't combat Covid-19. Now, more than ever, there is an urgent need to raise public awareness about the benefits of maintaining a healthy diet and to promote campaigns about how to avoid the onset of diabetes myelitis through lifestyle modifications.
Key Words:
Healthy Lifestyle, Pre-Diabetic, Compromised Immunity, SARS-CoV-2, Campaigns, Incidences, Prevalence
Introduction
The increase in the prevalence of diabetes mellitus around the world has become a public health concern. Obesity, a stationary lifestyle, and a rise in the population rate are the major factors contributing to diabetes mellitus (Benjamin et al., 2021).In Pakistan, a large percentage of the population is suffering from both type-I and type-II diabetes, and there are many complications associated with the diseases as a result of improper diagnosis, as well as a lack of awareness, which leads to non-compliance (Aamir et al., 2019).
As this disease is genetically transferred from parents to their offspring, the disease continues to run within the families for generations. The intake of an imbalanced diet has a significant impact on how our bodies respond to diseases. Insulin resistance, which affects approximately 92 percent of Pakistanis, is also one of the leading causes of diabetes, which is multifactorial. Increased body weight and body mass index, extra belly fat, a lack of physical exercise, smoking, and even cutting corners on sleep are the major factors that lead to insulin resistance (Imam and Ismail, 2017).
Heart diseases are major risk factors in diabetic patients. Type-2 diabetes is associated with metabolic disturbances such as insulin resistance, hyperglycemia, and abnormal hematologic complications, which demonstrate the severity and rapid development of coronary artery disease (Benjamin et al., 2021). Up to 80% of the death rate in diabetic patients is directly related to myocardial infarction and stroke, which may be due to thrombosis (Benjamin et al., 2021). Diabetes mellitus causes a significant range of genetic syndromes related to irregular chromosome numbers, such as Down's, Turner's, and Klinefelter’s syndromes, as well as diabetes insipidus and other conditions (Of et al., 2005).
Classification of diabetes:
• Type-1 diabetes (due to destruction of beta-cells by the body itself leading to decreased insulin level)
• Type-2 diabetes (decreased insulin function as body cells develop resistance against insulin)
• Gestational diabetes mellitus (occurs during the first 6 months of the pregnancy)
• Another type of diabetes (neonatal diabetes, due to pancreatic diseases, due to chemical secretions)
Type 1 and type 2 diabetes are known to be heterogeneous. Classification is essential as it is the basic step required to start the treatment, but sometimes there can be a case that is quite difficult to be categorized into either type (Care and Suppl, 2021a). There is a constant debate over how the progression of symptoms in adults and the presence of autoantibodies lead to Type-1 Diabetes Mellitus. Type-2 diabetes is caused by an abnormality of insulin production in the body (Care and Suppl, 2021a). In all types of diabetes, genetic and environmental factors disrupt beta-cell mass, resulting in Type-1 diabetes or abnormalities in their functioning, resulting in decreased insulin secretion, leading to Type-2 diabetes (Care and Suppl, 2021a). Type 1 and type 2 diabetes are known to be heterogeneous. Classification is essential as it is the basic step required to start the treatment, but sometimes there can be a case that is quite difficult to be categorized into either type (Care and Suppl, 2021a). There is a constant debate over how the progression of symptoms in adults and the presence of autoantibodies lead to Type-1 Diabetes Mellitus. Type-2 diabetes is caused by an abnormality of insulin production in the body (Care and Suppl, 2021a). In all types of diabetes, genetic and environmental factors disrupt beta-cell mass, resulting in Type-1 diabetes or abnormalities in their functioning, resulting in decreased insulin secretion, leading to Type-2 diabetes (Care and Suppl, 2021a).

Diagnosis
The diagnosis of diabetes can be made simply by measuring glucose levels in the blood (Care and Suppl, 2021a). During the Oral Glucose Tolerance Test, the Fasting Plasma Glucose test should be performed after at least 8 hours of fasting, i.e. > or equivalent to 126 mg/dL (7.0 mmol/L) and greater than or equal to 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) (Care and Suppl, 2021a). At least two irregular blood glucose level findings from two separate test samples or the same test sample are expected for a diabetes
diagnosis (Care and Suppl, 2021a).
Normal Plasma Ranges of Glucose
? Fasting Plasma Glucose should be from 100-125 mg/dL i-e (5.6-6.9 mmol/L) (Care and Suppl, 2021a).
? Plasma Glucose level measured two hours after meal ranges from 140-199 mg/L I-e (7.8-11.0 mmol/L) (Care and Suppl, 2021a).
? Patients with plasma glucose levels not in the diabetic range but high enough to be considered irregular are classified as pre-diabetic (Care and Suppl, 2021a).
Betain Level
Betain (glycin betain or TMG trimethylglycine) is needed for cell volume regulation. Betain is obtained from food and is also produced in mitochondria during choline oxidation (Lever et al., 2012).In 20% of diabetic patients, a high degree of Betain excretion by urine persists for years, resulting in inadequate betain levels, which can cause serious problems because betain is necessary and needed by cells to sustain or regulate cell volume, as well as to provide methyl groups for normal regulatory metabolism (Lever et al., 2012).
Prevalence and Estimation
According to data analyses and estimates for the year 2019, a vast number of individuals, i.e. 463 million people, are expected to have diabetes mellitus. Of this large number, half are unaware of their illness and condition (Of et al., 2005). The developing countries are ranked first in terms of the percentage of citizens with undiagnosed diabetes, accounting for 83.4 percent of diabetes prevalence worldwide (Of et al., 2005). After evaluating the statistics, it is predicted that by 2030, there would be up to 578 million people living with diabetes, and by 2045, this number would skyrocket to 700 million diabetic patients (Of et al., 2005).
Symptoms of Diabetes Mellitus
The identification of a particular disease is characterized by its symptoms appearing over time.
GI Symptoms
While considering the symptoms of diabetes mellitus, the most common symptoms that usually occur are associated with the GI tract as a result of hyperglycemia and autonomic neuropathy (Papatheodorou et al., 2018). Other findings that may be considered important in determining the mechanism of the GI symptoms are the time of diabetes persistence and psychiatric comorbidity that can be reversed by controlling the blood glucose level. Moreover, irregular cardiovascular reflexes are also observed in diabetes, which an important indication of disturbances in the abdominal vagus nerve (Papatheodorou et al., 2018).
Oral Symptoms
Studies also show that certain other symptoms marked in patients with diabetes are the oral symptoms firstly observed by SETFERT in 1862, after which many such cases were reported, though there is lacking evidence in the study of the exact underlying mechanism and the link between periodontal disease and diabetes (Gruji? and Petronijevi?-Novak, 1988). There may be the reason that due to increased DMF (decayed, missed due to decay, and filled teeth)-mean values in patients with diabetes (Gruji? and Petronijevi?-Novak, 1988). Diabetes cannot be considered as a direct reason for periodontal diseases, but a systemic promoting factor, creating favorable conditions for local agents promotes gingivitis and periodontitis. Poor oral hygiene in diabetes is mainly responsible for the development of periodontal disease (Gruji? and Petronijevi?-Novak, 1988).
Psychological Disturbances
Studies show that GI Symptoms in diabetes and psychological effects are inter-linked. Women having type 1 diabetes had more anxiety and depression and lower quality of life than men, but appropriate controls were not included, and GI symptoms were not specifically addressed, but more commonly, Psychological factors are predominately observed in non-diabetic patients with GI disorders (Talley et al., 2001).
Figure 2: Most commonly occurring Diabetes symptom
Complications of Diabetes Mellitus
According to an estimate, approximately half of the diabetes cases are not diagnosed in time, raising the risk of complications. Microvascular and macrovascular complications are the two primary forms of diabetic complications (Papatheodorou et al., 2018).
Microvascular complications comprise neuropathy, nephropathy, and retinopathy, while macrovascular complications include coronary disorders, stroke, and peripheral artery disease (Papatheodorou et al., 2018). Neuronal injury, nephron damage resulting in kidney problems, heart disease, and other complications are all commonly observed in diabetic patients (Verhulst et al., 2019). These disruptions can also cause the release of reactive oxygen species, which may cause inflammation. Diabetes has a significant impact on vascularized tissues and organs, such as the eyes, endothelial cells, kidneys, and nerves (Verhulst et al., 2019).
Microvascular Complications
Diabetic kidney disease (DKD) and peripheral neuron injury are two of the most common microvascular complications (Forbes and Fotheringham, 2017).
Macrovascular Complications
DKD may also contribute to the development of macrovascular disorders such as atherosclerosis, congestive heart failure (CHF), heart attacks, and brain damage (Forbes and Fotheringham, 2017).
Epidemiology and Pathogenesis
Latest studies have shown that the underlying cause of the elevated mortality and morbidity rate of type-1 diabetes is the poor economic condition of most of the people of our country. Obesity has also been identified as a major factor in reducing insulin sensitization in our body cells, ultimately leading to type 2 diabetes (Papatheodorou et al., 2018).
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is another significant complication of diabetes, with a rising incidence rate contributing to coronary damage and a high rate of mortality. Patients with diabetes have a higher risk of AF, although there are some ambiguities about the age, sex, and type of diabetes, as well as the prevalence of Atrial fibrillation (Bisson et al., 2021).In chronic diabetes mellitus, a foot ulcer, in addition to peripheral neuropathy, is a common occurrence, usually resulting in a lack of sensation in the affected region and requiring surgical removal of the leg (Papatheodorou et al., 2018). According to studies, patients with diabetes type 2, obesity, hypertension, and insulin tolerance are more likely to experience AF, with a higher rate of females with diabetes type 2 and older males with or without diabetes (Bisson et al., 2021).

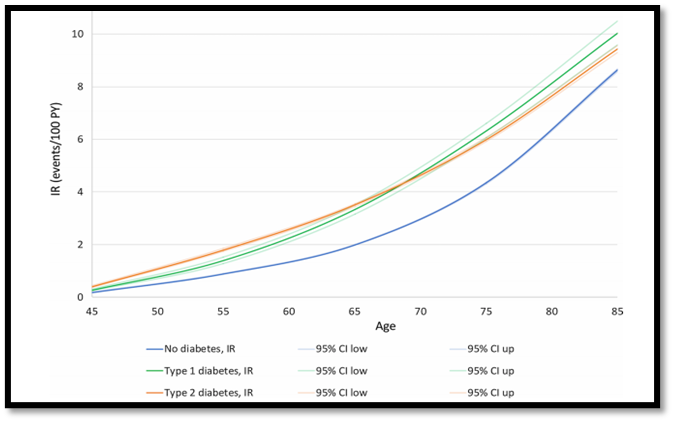
Incidence rate of atrial fibrillation w.r.t age and types of diabetes (Bisson et al., 2021)
Diabetes may also be brought about as a result of a failed pregnancy increase in weight with age and reduced insulin synthesis in older females were cited as the main contributing factors (Bisson et al., 2021).

Rate of diabetes in 3 trimesters (Forbes and Fotheringham, 2017)
Though most countries have adopted methods to control and reduce the incidence of diabetes complications, the number of new cases has not stayed constant, resulting in a little to no significant improvement in the treatment of diabetes complications (Forbes and Fotheringham, 2017). While we invest time and resources in treating the most prominent causative factors, we should also shift our attention to the goal of the control and management of the disease (Forbes and Fotheringham, 2017). It has been proven that only one out of every 100 therapies discovered to treat diabetes clears the clinical trial (Forbes and Fotheringham, 2017).
Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus in Pakistan Outlining rate of Occurrence of Diabetes in Pakistan
In the International Diabetes Federation (IDF), diabetes atlas 2017 ranking, Pakistan occupies 10th position out of 221 countries of the world is a low- medium-income country (Aamir et al., 2019). Diabetes affects about 7.5 million individuals between the ages of 20 and 79. Furthermore, according to the World Health Organization (WHO) diabetes country profiles 2016, Pakistan lacks a national response to diabetes, as well as an organizational strategy, national diabetes recommendations, and a diabetes registry (Adnan and Aasim, 2020). Diabetes has become a potentially damaging severe disease due to multiple heterogeneous factors, requiring to give huge public health attention by health care systems across the world (Mehmood and Junaid, 2018).
Type 2 diabetes mellitus affects 12% of the population in Pakistan (T2DM). Patients with undiagnosed and untreated diabetes have a higher risk of premature mortality and severe macrovascular complications. Microvascular complications are also common in Pakistani people with diabetes, as shown by the extent to which they occur. A few instances include retinopathy (58.0%), neuropathy (39.5%), and nephropathy (61.4%) (Mehmood and Junaid, 2018).
The last national diabetes survey in Pakistan was conducted in 1999 (published in 2007), according to which the oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) revealed that type 2 diabetes was present in 11% of the population. The International Diabetes Federation (IDF) estimated the prevalence of diabetes in Pakistan to be 6.8% among people aged 20 to 79 years old in its Atlas 5th edition, but healthcare workers with deeper perception always believed this to be inaccurate. As a result, there was a contradiction in findings of the range from7.2% to 19.21% in multiple areas of Pakistan (Aamir et al., 2019).
Pakistan has a high prevalence of undiagnosed type 2 diabetes. Undiagnosed diabetes was found in 6.4 percent of outpatients seeking primary care in the major cities of Pakistan (Aamir et al., 2019). The three considerable risk factors highlighted were BMI >23.0 kg/m2, less physical activity, and inherited history of Diabetes mellitus Type 2. In the newly diagnosed T2DM (Diabetes mellitus Type 2), patients were counselled to improve their lifestyle along with supplements of OAD (oral anti-diabetic drug)(Aamir et al., 2019). Biguanide and Sulphonyl urea were the most frequently recommended OADs. In 45.1 percent of patients, the dosage regimen began with two OADs, and in 9.5 percent of patients, it started with insulin. Keeping track of HbA1c and FBG (fasting blood glucose) for three months resulted in a substantial drop of 1.6 percent in HbA1c and 41.9mg/dL in FBG (fasting blood glucose) (Mehmood and Junaid, 2018).

Factors and occurrence of prediabetes, non-diabetes, and diabetes rate (n=18, 856)
To test the diabetes mellitus type II prevalence in the community of Pakistan, a broad survey was performed using a screening test called glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) in 2018. This research is centred on various statistical categories as well as all the regional domains of Pakistan (Aamir et al., 2019) .The root causes leading to complications in diabetes proved to be the unawareness of the public, inappropriate diagnosis and treatment strategies, and most importantly the non-compliance of patients to the therapy (Aamir et al., 2019). According to the 9th edition of the IDF Diabetes Atlas, the rate of occurrence of diabetes in Pakistan has reached 17.1%, which is 14.8 percent higher than previous estimates (Saeedi et al., 2019). Diabetes affected about 19 million people in Pakistan in 2019, placing them at a high risk of life-threatening complications. About 8.5 million of these 19 million people are undiagnosed and on the brink of death (Saeedi et al., 2019)
Health Expenditure and Financial Load
Due to the great turnover from infectious to non-communicable diseases, causing a great financial load on the economy for the expenditure of money on health care systems. Among the greatest hardships faced by the government in providing accurate quality facilities, maintaining the medical infrastructure, skilled workers, and the medication expenses are the ultimate reasons for great money usage (Datta, Husain, and Asma, 2019). Pakistan is among the most densely populated LMICs (lower-middle-income countries), with a population of 195 million people, where NCDs are a serious health problem (Datta, Husain and Asma, 2019).
Treating non-communicable diseases (NCDs) in lower, middle-income countries (LMICs) is not cost-effective and exposes tribes to economic challenges and risks. In Pakistan, there is a correlation between medication expenditure for two significant NCDs: hypertension (blood pressure) and diabetes. The financial costs of diabetes and its related complications have resulted in great upthrust in the overall healthcare spending by the patients. In Pakistan, the current yearly medical costs for a single diabetic patient were calculated to be Pakistani rupees (PKR) 11,580 (US$ 197) (Mehmood and Junaid, 2018).

Total Average Cost Spent on Diabetes Mellitus in Pakistan
Prominent Factors and Reasons Causing Diabetes Mellitus in Pakistan
LMIC medical care service is unable to deal with the growing challenge of non-communicable diseases (NCDs), resulting in little or restricted approach for the achievement of NCD prevention and diagnosis (Datta, Husain and Asma, 2019). The decreased trend of patient-physician counselling interaction in Pakistan leads to unsatisfied patients not adhering to their treatment or therapy, making them vulnerable to a further complication of the disease (Gillani et al., 2018).
Many people live their whole lives without proper diagnosis and identification of disease, which is also multifactorial, like unawareness, poverty, illiteracy, insufficient resources, and inappropriate follow-up. In addition to being a clinical specialist, physicians' professional abilities should include: maintaining an adequate level of expertise, the capability to recognize and diagnose, implementing patient care processes, prescribing medications, and staying up to date with the new medical innovations (Gillani et al., 2018).
Furthermore, accurate contact with patients is critical to the long-term effectiveness of these procedures. The purpose of the patient's appointment is to re-visit the doctor (Gillani et al., 2018). Discontented patients are more likely to stop asking for professional advice from a specialist they believe is inept, according to experimental evidence. Unsatisfied patients are also notorious for taking a long time to get a doctor's appointment or taking medication on their own (Gillani et al., 2018).
According to a recent Survey, Pakistan received the lowest score of five points on the International Doctor-Patient Interaction Analysis paper in 2011, while Ireland received the highest score of 66 points (Gillani et al., 2018). HbA1c is a safe and efficacious test to be performed in the community areas in middle-income and low-income countries, and it has a good relation with 2-hour OGTT (Lin et al., 2020).
There should be a devised policy in middle-income and low-income countries for shifting focus from expensive treatments towards the prevention, diagnosis, and control of NCD to protect people from diabetes complications (Lin et al., 2020).

Figure 7: Trend and Reasons for Diabetes Mellitus in 195 Countries from 1990-2025
Diabetes and Covid-19 Why are people with diabetes myelitis at higher risk of developing the infection during the Covid-19 pandemic?
Although diabetics have the same rate of getting infected with the severe acute respiratory syndrome corona virus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) as the rest of the population getting exposed to the virus still, they are advised to be extra cautious. This is because the fatality rate of Covid-19 is found out to be four times the normal in patients suffering from diabetes myelitis type-2, and is about twice in patients with type-1 diabetes, which may be because diabetes is often associated with other health issues like high blood pressure and obesity making it difficult for the person to fight against the coronavirus infection (Morris, 2020).
Why do Diabetics have Higher ACE-2 Levels?
The levels of ACE-2 are much higher in diabetics and hypertensive patients than the normal individuals who are either due to hyper-activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) or continuous intake of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs). The upregulation of ACE-2 levels due to enhanced gene expression of ACE-2 in response to the prolonged use of ACE inhibitors has been evident from various animal studies, but no such evidence is obtained from human studies, so the reason as to why the diabetics show an increase in ACE-2 levels is still a bit unclear (Sacks et al., 2020).
How Diabetes Myelitis Affects the Prognosis of Coronavirus Infection?
Type 2 diabetes patients tend to have elevated levels of plasminogen and furin, which are believed to enhance the pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2. This is because to enter a human cell; the coronavirus requires binding to angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE-2) and Furin proteins expressed on the cell surface. Having elevated levels of both ACE-2 and Furin proteins, diabetics are at a great disadvantage when it comes to the entry of SARCoV-2 into their cells (Sacks et al., 2020). Consistently elevated blood sugar levels of diabetics impair the capacity of their body cells to repair themselves and also diminishes the response of their immune cells, especially T-cells and natural killer cells, resulting in a reduction in viral clearance from cells and a worsening of the infection (Gupta, Hussain and Misra, 2020).
Hyperglycemia also boosts the number of adhesion molecules expressed on the epithelial lining, which in turn reduces the penetration of neutrophils to the infection site, thus decreasing the phagocytic activity of the immune cells (Sacks et al., 2020).
The risk of complications related to coronavirus infection is usually higher in older diabetic patients with poor glycemic control than younger patients with well-controlled sugar levels (Hussain, Bhowmik and do Vale Moreira, 2020).
Excess abdominal fat is common in patients with type-2 diabetes myelitis, making it difficult for the diaphragm to flatten entirely during inspiration. Incomplete diaphragm contraction leads to the failure of sufficient lung expansion, and if the lungs don't expand fully, the gaseous exchange is reduced, and blood cannot be oxygenated properly (Buras et al., 2019).
As in the case of Covid-19 infection, the lung tissue is severely damaged and is often saturated with mucous. So, inadequate lung expansion as a result of decreased diaphragm contraction combined with reduced gaseous exchange due to alveolar depletion may result in extreme hypoxia, requiring artificial ventilation and admission to an intensive care unit (ICU) (Das et al., 2020).
Moreover, there is also an over-expression of ACE-2 in the adipose tissues, which would also increase the viral entry in these tissues (Ng and Rickard, 2020).
Diabetic patients are also more likely to develop thrombophilia due to an imbalance in the concentration of the clotting factor, which may be exacerbated by the covid-19 virus, as it elevates the clotting activity even further (Hussain, Bhowmik and do Vale Moreira, 2020).

Does Covid-19 Infection Lead to a Hyperglycemic State?
SARS-CoV-2 is also known to attack and destroy the insulin-producing beta-cells of the pancreas, thus further reducing the level of insulin and leading to elevated blood glucose levels even in people not having diabetes before and if these high blood sugar levels are not controlled in time, can proceed to ketoacidosis and diabetic nephropathy (Das et al., 2020; Ng and Rickard, 2020).
Which Anti-Diabetic Drugs are Safe to be Continued in the Covid-19 Infection?
A study showed that patients with SARCoV-2 infection who were treated with Metformin had a better prognosis of the disease and a significantly lower chance of mortality than people who were treated with any other anti-diabetic medication. Thiazolidinediones (TZD), on the other hand, are specifically prohibited from being given to covid-19 patients for the treatment of diabetes as it can lead to pneumonia and thus worsening the lung condition even more (Das et al., 2020).
Treatment with the usual anti-diabetics can be continued in patients with mild covid-19 infection and well-controlled blood sugar levels. If a patient is previously treated with sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT-2), then the patient may be switched to other medication to prevent the risk of severe dehydration. ACE inhibitors and ARBs also need to be stopped during coronavirus infection as they can lead to the up-regulation of ACE-2 (Das et al., 2020).
Monitoring of the Blood Sugar Levels During Covid-19 Infection
As covid-19 infection has been shown to elevate the normal blood glucose level even in non-diabetics, so it is quite essential to critically monitor the blood sugar levels of diabetics infected with SARS-CoV-2. As the patients cannot visit the hospitals frequently to get their glucose level tests during the pandemic, they should be advised to buy the glucose monitor and keep a check of their glucose level during the covid-19 infection to prevent any complication related to hyperglycemia. Type-1 diabetes patients should also continue administering insulin and maintain their glucose levels during the quarantine (Das et al., 2020).
Figure 8: COVID-19 and Risk Groups
Management of Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes Mellitus is the most common disease worldwide and the fifth leading cause of mortality. The increasing rate of type 2 diabetes mellitus can cause major complications such a kidney failure, heart failure, stroke, and blindness. So, Diabetes self-management education can produce a positive impact on a patient’s behavior and patient’s health (Kumah et al., 2021).

Self-Management Education (SME)
It is a tool that helps patients to optimize the blood glucose level by providing awareness and increase patient’s knowledge to manage diabetes (Kumah et al., 2021). It provides behavioral strategies to manage diabetes. Educational sessions are arranged for the patients ranging from brief instructions to comprehensive and formal programs by the physician or Nurse or a Dietician (Kumah et al., 2021). SME improves the patient quality of life and decreases the total cost of treatment of diabetes. It also results in weight loss, better glucose control, decrease blood pressure, and better diet and exercise habits (Kumah et al., 2021).
Diabetes Care Models
Different models of diabetes care exist in the health care setting. One of which is the service provided by diabetologists and endocrinologists. While the most common model is primary care provided by the physician. Nurses and dieticians also provide services to diabetic patients under the supervision of specialists (Kumah et al., 2021). Other models that provide service to diabetic patients include the Clinical pharmacist-led model and nurse-led model (Kumah et al., 2021). Due to the complex nature of diabetes, the literature suggests a team approach service for diabetes treatment. This care model involves a range of health care providers such a primary care physician, dietician, diabetologist, Nurse, and pharmacists to integrate their skills to improve the patient's quality of life (Kumah et al., 2021).
Early Diagnosis by Multifocal Electroretinogram
Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) is a condition that affects the eyes and causes blindness (Huang et al., 2021). All the therapies such as Laser photocoagulation, intraocular drug injection, and vitrectomy are the major therapies used to treat Diabetic Retinopathy (Huang et al., 2021). These therapies slow down the progression of the disease and cannot reverse the loss of vision (Huang et al., 2021).
Figure 9: Determining Blood Glucose level
Multifocal Electroretinogram noninvasive method to detect retinal function. It detects the changes that occur in the retinal function before the occurrence of diabetic damage to the retina. It provides significant evidence for clinical studies (Huang et al., 2021). Clinical study of 76 type 2 diabetes patients with no apparent retinopathy (age 64 ± 8 years) and 64 normal eyes from thirty-two healthy control (age 65 ± 5 years) were randomly examined by using multifocal electroretinogram. All eyes have 16/20 visual acuity without exudation in the retina. Patients with glaucoma were excluded from the list (Huang et al., 2021).
Mobile Health
The field of Information Technology has been applied to the health care system. It follows the medical guidelines. Mobile Health provides special services such as short message service (SMS), wearable technology, and smartphone applications (Shan, Sarkar and Martin, 2019).
Mobile Health is well suited in the management of diabetes mellitus as it provides frequent contact with patients and provides information about Glucose control level and self-management. Many device manufacturers have manufactured wearable glucose meters, e.g., Accu-Chek connects blood glucose meter. It calculates blood glucose and insulin levels and the dietary intake of carbohydrates. The blood glucose level data is presented to the patients for self-management. It provides real-time continuous glucose monitoring (Shan, Sarkar and Martin, 2019).
The BlueStar mobile Diabetes coach is the first type-2 diabetes app available on prescription and non-prescription versions. It was approved by the FDA in 2017 (Shan, Sarkar and Martin, 2019). Diabeo, DID, BlueStar, and MITI are the apps that provide access to a remote clinician. The clinician/physician assesses the patient’s data and provides treatment or guidelines accordingly. It provides the easiest way of communication between patients and physicians. The physician also provides motivation and education through such apps (Shan, Sarkar and Martin, 2019).
Exercise Effect on Diabetes
Regular exercise help in the prevention of diabetes and is also effective in the treatment of type 2 diabetes by lowering blood glucose levels. Although the mechanism of insulin action after the exercise is unclear, it is considered that the gene responsible for Insulin signalling could be mediated by exercise and training. Endurance training increases neuromuscular surface area, synaptic fold, and Ach receptor number. It also improves Ach activity and increases the release of Ach (Joseph, Parvathy and Varma, 2021).
Physical exercise promotes glucose uptake and improves insulin's sensitization of the cells. (Joseph, Parvathy and Varma, 2021). In Pakistan, we mostly take a diet rich in carbohydrates, so clinical studies suggest that diet-induced hyperinsulinemia results in impaired insulin signalling, impaired glucose transport, and metabolism (Joseph, Parvathy and Varma, 2021). According to the results of a clinical study, it has been found that in Pakistan majority of the population take a carbohydrate-rich diet which leads to impaired insulin signalling and lower glucose transport into the cells leading to high blood glucose levels, so the most effective approach to improve insulin resistance and decrease cardiovascular risks is that the person should change their lifestyle. So, the study reinforces the importance of regular exercise (Joseph, Parvathy and Varma, 2021).
Figure 10: Management of diabetes
Pharmacological and Non-Pharmacological Treatment of Diabetes
Pharmacological Approach
Herbal Treatment
More than 250 plant species have been identified for their hypoglycaemic properties in numerous studies documented up till now. Momordica charantia (bitter gourd) is one of the plants that has been tested for its anti-diabetic effects in both humans and animals. However, later animal experiments have shown the opposite results. Then it was concluded that the hypoglycaemic effect of Bitter gourd was due to the depletion of gluconeogenic enzymes (causes the generation of glucose from non-carbohydrate carbon) and due to the stimulation of skeletal muscle cells causing increased uptake of glucose. Bitter gourd administration may be useful as a supplementary therapy to lessen the effects of insulin or other hypoglycaemic drugs or plants in the management of diabetes if it can be assumed that animal studies can be applied to human beings (Liu et al., 2021).
From the studies done in the past few years, It has been evident that the plants like Amelanchier alnifolia, Dillenia indica, and Chrysophyllum albidum have glucose-lowering properties (Zhao et al., 2021).
Sulfonylureas
It was discovered in the twentieth century that certain sulphonamides have a blood glucose-lowering effect on lab animals, which led to the development of the class of sulfonylureas, which are now used to treat diabetic patients (Yu, 2020).
Also, in severe infections like the coronavirus, there is a poor caloric intake, so in this case, hypoglycaemic action is produced by sulfonylureas (Ugwueze et al., 2020).

Insulin Analogues
In hospitals, for hyperglycaemic patients, insulin, along with constant monitoring of glucose, is the first choice of treatment (Longo et al., 2020). For type-1 and advanced type-2 diabetic patients, several different insulin analogues are available (Sena et al., 2010). Insulin formulations are categorized based on the duration of action and the time at which they are given, such as intermediate-acting/long-acting insulin given at bedtime versus rapid-acting insulin given before meals, and are manufactured from humans, porcine, or bovine insulin or a combination of porcine and bovine both (Care and Suppl, 2021b).
It was also seen in 25 patients suffering from diabetes along with COVID-19 that insulin has better glycaemic control in those patients as it causes the suppression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and also boosts the immune mediators (Ugwueze et al., 2020).
Metformin
Metformin, an insulin sensitizer, is thought to be the first line of therapy for hyperglycemia. It has hypoglycaemic properties as it lowers blood glucose levels, inhibits hepatic glycogenesis, and improves insulin-stimulated glucose absorption. It reduces insulin resistance in muscle tissues and the liver and disrupts adipose tissue lipolysis, lowering FFA levels in the blood. When administered as a single treatment, Metformin lowers HbA1C by 1.5 percent. It also improves lipid profiles and lowers blood pressure (Aroda and Ratner, 2018).
Metformin activates the adenosine monophosphate kinase enzyme, causing phosphorylation of the ACE2 receptor, which is responsible for SARS- COV-2's entry into human cells. Phosphorylation renders ACE2 receptors inactive (Longo et al., 2020).
DPP4 Inhibitors
It has anti-inflammatory effects, which means it decreases or negates the effect of COVID-19 on hyperglycemia regulation (Ugwueze et al., 2020).
Meglitinides
Nateglinide belongs to the meglitinides class. It binds to the same site that sulphonylurea, its derivatives, and repaglinide bind to, causing insulin release (rapid and short-term insulin release)- but in a more specific way (Sena et al., 2010).
They lower blood sugar levels while increasing fasting hyperglycemia (Sena et al., 2010).
Pramlintide (Human Amylin Analogue)
Pramlintide (subcutaneously injected before meals) is licensed as a supplement to insulin therapy in the United States (Sena et al., 2010)
It produces a 0.5-0.7 percent decrease in HbA1C and a 0.5-0.7 percent decrease in body weight (satiety effect) (Sena et al., 2010).
Non-Pharmacological Approach
Exercise and Diet:
Regular workout, changes in diet, and glycaemic index control is needed for the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus, as overweight and other metabolic disorders (insulin resistance syndrome) are the primary causes of type 2 diabetes mellitus (Leite et al., 2020).
Sugars and Sweeteners
Saccharin, aspartame (rarely used since it is highly sweet and even a very small amount is enough), cyclamate, and acesulphame K are sweeteners used in beverages and food, which is convenient for diabetic patients as they lead to less caloric intake (Leite et al., 2020).
In the past, naturally occurring sweeteners such as fructose and sorbitol were commonly used by diabetic patients, but it has now been discovered that monosaccharides and disaccharides can worsen glycaemic regulation or raise lipid levels in some circumstances (Leite et al., 2020).
Folic Acid
For diabetic patients, sufficient folate intake is necessary. In 1998, the RDA for folic acid was increased from 200 to 400 mg a day (Leite et al., 2020).
Transplantation Therapies
Pancreas Transplantation
Pancreas transplantation is used for treating or handling diabetic patients with normal renal function because it improves glucose metabolism. Mentioned below are some of the benefits of pancreatic transplantation:
1)It improves people's quality of living.
2) Prevent nephropathy in diabetics.
3) Blood glucose levels are not needed to be monitored daily.
4) Normalization of HbA1C.
5) Reduces dietary restrictions.
6) No more secondary complications (Aref et al., 2019).
The key drawbacks of pancreas transplantation are the need for immunosuppression and other harmful or side effects (Aref et al., 2019).
Islets of Langerhans Transplantation
Another strategy for controlling blood glucose levels is islet transplantation. Donor islets are isolated and injected into the recipient's portal vein using a percutaneous catheter (Aref et al., 2019).
Conclusion
The proper and prompt diagnosis of a disease is the very first step in reducing its dissemination and exterminating it entirely.
Most people having persistent diabetes are not even aware of their present illness leading to serious complications and even death. The secret to better diabetes care is to stop blaming the government for not investing enough money in services and hospitals, and instead take personal responsibility for changing our lifestyles by eating a healthy diet, incorporating physical exercise in our everyday routine, and reducing our fat and sugar intake. As members of the healthcare sector, we can educate the general population about disease outcomes and symptoms by organizing public awareness campaigns, seminars, and workshops, as well as assisting individuals in being self-sufficient.
References
- Aamir, A. H. et al. (2019) 'Diabetes Prevalence Survey of Pakistan (DPS-PAK): Prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus and prediabetes using HbA1c: A popula#on-based survey from Pakistan', BMJ Open, 9(2), pp. 1-9. DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-025300.
- Adnan, M. & Aasim, M. (2020) 'Prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus in adult popula#on of Pakistan: A meta-analysis of prospec#ve cross-sec#onal surveys', Annals of Global Heal!, 86(1), pp. 1-8. DOI: 10.5334/aogh.2679.
- Aref, A. et al. (2019) 'Pancrea#c transplanta#on: Brief review of !e current evidence', World Journal of Transplanta#on, 9(4), pp. 81-93. DOI: 10.5500/wjt.v9.i4.81.
- Aroda, V. R. & Ratner, R. E. (2018) 'Metformin and type 2 diabetes preven#on, Diabetes Spectrum, 31(4), pp. 336-342. DOI: 10.2337/ds18-0020.
- Benjamin, B. K. et al. (2021) 'The Associa#on between Type-2 Diabetes Dura#on and Major Adverse Cardiac Events after Percutaneous Coronary Interven#on', 2021.
- Bisson, A. et al. (2021) 'Sex, age, type of diabetes and incidence of atrial fibrilla#on in pa#ents wi! diabetes mellitus: a na#onwide analysis', Cardiovascular Diabetology. BioMed Central, 20(1), pp. 1-11. DOI: 10.1186/s12933-021-01216-7.
- Buras, E. D. et al. (2019) ‘Fibro-adipogenic remodeling of !e diaphragm in obesity - associated respiratory dysfunc#on', diabetes, 68(1), pp. 45-56. DOI: 10.2337/db18-0209.
- Care, D. & Suppl, S. S. (2021a) '2. Classifica#on and Diagnosis of Diabetes : .andards of Medical Care in Diabetes d 2021', 44(January), pp. 15-33. DOI: 10.2337/dc21-S002.
- Care, D. & Suppl, S. S. (2021b) 'Pharmacologic approa'es to glycemic treatment: .andards of medical care in diabetesd2021', Diabetes Care, 44(January), pp. S111-S124. DOI: 10.2337/dc21-S009.
- Das, S. et al. (2020) 'Since January 2020 Elsevier has created a COVID-19 resource center wi! free informa#on in English and Mandarin on !e novel coronavirus COVID - 19. The COVID-19 resource center is hosted on Elsevier Connect, !e company's public news and informa#on ', (January).
- Da(a, B. K., Husain, M. J. & Asma, S. (2019) 'Assessing !e rela#onship between out - of-poet spending on bl*d pressure and diabetes medica#on and household catastrophic heal! expenditure: Evidence from Pakistan', Interna#onal Journal for Equity in Heal!. Interna#onal Journal for Equity in Heal!, 18(1), pp. 1-12. DOI: 10.1186/s12939-018-0906-x.
- Forbes, J. M. & Fo!eringham, A. K. (2017) ‘Vascular complica#ons in diabetes: old messages, new !oughts', Diabetologia. Diabetologia, 60(11), pp. 2129-2138. DOI: 10.1007/s00125-017-4360-x.
- Gillani, A. H. et al. (2018) 'Direct and indirect cost of diabetes care among pa#ents wi! type 2 diabetes in private clinics: a mul#center study in Punjab, Pakistan', Expe) Review of Pharmacoeconomics and Outcomes Resear'. Taylor and Francis Ltd, 18(6), pp. 647-653. DOI:10.1080/14737167.2018. 1503953.
- Grujić, M. & Petronijević-Novak, S. (1988) ‘[Dental and oral aspects of diabetes mellitus].', .omatoloski glasnik Srbije, 24(1), pp. 39- 44. Available at
- Gupta, R., Hussain, A. & Misra, A. (2020) 'Diabetes and COVID-19: evidence, current status, and unanswered resear' questions', European Journal of Clinical Nutri#on. Springer US, 74(6), pp. 864-870. DOI: 10.1038/s41430-020-0652-1
- Huang, J. et al. (2021) 'Mul#focal Electrore#nogram Can Detect !e Abnormal Re#nal -ange in Early .age of type2 DM Pa#ents wi!out Apparent Diabe#c Re#nopa!y', 2021.
- Hussain, A., Bhowmik, B. & do Vale Moreira, N. C. (2020) 'COVID-19 and diabetes: Knowledge in progress', Diabetes Resear' and Clinical Prac#ce. The au!or (s), 162, p. 108142. DOI: 10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108142.
- Imam, M. U. & Ismail, M. (2017) 'The Impact of Tradi#onal F*d and Lifestyle Behavior on Epigene#c Burden of -ronic Disease', Global -allenges, 1(8), p. 1700043. DOI: 10.1002/g'2.201700043.
- Joseph, A., Parva!y, S. & Varma, K. K. (2021) ‘Hyperinsulinemia Induced Altered Insulin Signaling Pa!way in Muscle of High Fat- and Carbohydrate-Fed Rats : Effect of Exercise', 2021.
- Kumah, E. et al. (2021) 'Review A)icle Influence of !e Model of Care on !e Outcomes of Diabetes Self- Management Educa#on Program : A Scoping Review', 2021.
- Leite, R. G. O. F. et al. (2020) 'Effec#veness of non- pharmacological strategies in !e management of type 2 diabetes in primary care: A protocol for a systema#c review and network meta-analysis', BMJ Open, 10(1), pp. 1-7. DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019- 034481.
- Lever, M. et al. (2012) 'Variability of plasma and urine betaine in diabetes mellitus and its rela#onship to me!ionine load test responses : an observa#onal study', pp. 1- 8.
- Lin, X. et al. (2020) 'Global, regional, and na#onal burden and trend of diabetes in 195 countries and territories : an analysis from 1990 to 2025', Scien#fic Repo)s. Nature Publishing Group UK, (0123456789), pp. 1-11. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-71908-9.
- Liu, Z. et al. (2021) 'The Effect of Momordica 'aran#a in !e Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus: A Review', Evidence-based Complementary and Alterna#ve Medicine, 2021. DOI: 10.1155/2021/3796265.
- Longo, M. et al. (2020) 'Trea#ng type 2 diabetes in COVID-19 pa#ents: The poten#al benefits of injec#ve !erapies', Cardiovascular Diabetology. BioMed Central, 19(1), pp. 1- 5. DOI: 10.1186/s12933-020-01090-9.
- Mehm*d, K. & Junaid, N. (2018) ‘Prevalence of undiagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus in Pakistan: Results of SCREEN-diabetes disease registry', Journal of !e Pakistan Medical Associa#on, 68(8), pp. 1171-1178.
- Morris, D. (2020) ',at is !e effect of COVID-19 on people wi! diabetes?', Independent Nurse, 2020(5), pp. 12-17. DOI: 10.12968/indn.2020.5.12.
- Ng, K. E. & Riard, J. P. (2020) 'The Effect of COVID-19 on Pa#ents Wi! Diabetes', diabetes, 45(11), pp. 9-12.
- Of, C. et al. (2005) 'DIABETES MELLITUS AND OTHER CATEGORIES OF DESCRIPTION OF DIABETES', 28.
- Papa!eodorou, K. et al. (2018) 'Complica#ons of Diabetes 2017', Journal of Diabetes Resear', 2018. DOI: 10.1155/2018/3086167.
- Sas, L. J. et al. (2020) 'Considera#ons for people wi! diabetes during !e Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) pandemic', Diabetes Resear' and Clinical Prac#ce. Elsevier B.V., 166, p. 108296. DOI: 10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108296.
- Saeedi, P. et al. (2019) 'Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projec#ons for 2030 and 2045: Results from !e Interna#onal Diabetes Federa#on Diabetes Atlas, 9! edi#on', Diabetes Resear' and Clinical Prac#ce. Elsevier Ireland Ltd, 157, p. 107843. DOI: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843.
- Sena, C. M. et al. (2010) ‘Diabetes mellitus: New 'allenges and innova#ve !erapies', EPMA Journal, 1(1), pp. 138-163. DOI: 10.1007/s13167-010-0010-9.
- Shan, R., Sarkar, S. & Ma)in, S. S. (2019) 'Digital heal! te'nology and mobile devices for !e management of diabetes mellitus : state of !e a)'. Diabetologia, pp. 877-887.
- Talley, N. J. et al. (2001) ‘Psy'ological distress is linked to gastrointestinal symptoms in diabetes mellitus' American Journal of Gastroenterology, 96(4), pp. 1033-1038. DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9270(00)02398-4.
- Ugwueze, C. V. et al. (2020) ‘COVID-19 and Diabetes Mellitus: The Link and Clinical Implica#ons', Dubai Diabetes and Endocrinology Journal, 26(2), pp. 69-77. DOI: 10.1159/000511354.
- Verhulst, M. J. L. et al. (2019) 'Evalua#ng all poten#al oral complica#ons of diabetes mellitus', Fron#ers in Endocrinology, 10(FEB). DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00056.
- Yu, M. (2020) 'The Place of Sulfonylureas in !e Evolving Landscape of Combina#on Therapy', Diabetes Therapy. Springer Heal!care, 11(s1), pp. 23-28. DOI: 10.1007/s13300-020-00813-1.
- Zhao, R. et al. (2021) 'Nontradi#onal Therapy of Diabetes and Its Complica#ons', Journal of Diabetes Resear', 2021, pp. 1-5. DOI: 10.1155/2021/1592049.
Cite this article
-
APA : Khan, R., Hussain, M., & Shehzadi, K. (2016). A Synopsis of the Current Scenario of Diabetes Mellitus in Pakistan. Global Immunological & Infectious Diseases Review, I(I), 21-35. https://doi.org/10.31703/giidr.2016(I-I).03
-
CHICAGO : Khan, Rumla, Murtaza Hussain, and Kiran Shehzadi. 2016. "A Synopsis of the Current Scenario of Diabetes Mellitus in Pakistan." Global Immunological & Infectious Diseases Review, I (I): 21-35 doi: 10.31703/giidr.2016(I-I).03
-
HARVARD : KHAN, R., HUSSAIN, M. & SHEHZADI, K. 2016. A Synopsis of the Current Scenario of Diabetes Mellitus in Pakistan. Global Immunological & Infectious Diseases Review, I, 21-35.
-
MHRA : Khan, Rumla, Murtaza Hussain, and Kiran Shehzadi. 2016. "A Synopsis of the Current Scenario of Diabetes Mellitus in Pakistan." Global Immunological & Infectious Diseases Review, I: 21-35
-
MLA : Khan, Rumla, Murtaza Hussain, and Kiran Shehzadi. "A Synopsis of the Current Scenario of Diabetes Mellitus in Pakistan." Global Immunological & Infectious Diseases Review, I.I (2016): 21-35 Print.
-
OXFORD : Khan, Rumla, Hussain, Murtaza, and Shehzadi, Kiran (2016), "A Synopsis of the Current Scenario of Diabetes Mellitus in Pakistan", Global Immunological & Infectious Diseases Review, I (I), 21-35
-
TURABIAN : Khan, Rumla, Murtaza Hussain, and Kiran Shehzadi. "A Synopsis of the Current Scenario of Diabetes Mellitus in Pakistan." Global Immunological & Infectious Diseases Review I, no. I (2016): 21-35. https://doi.org/10.31703/giidr.2016(I-I).03
